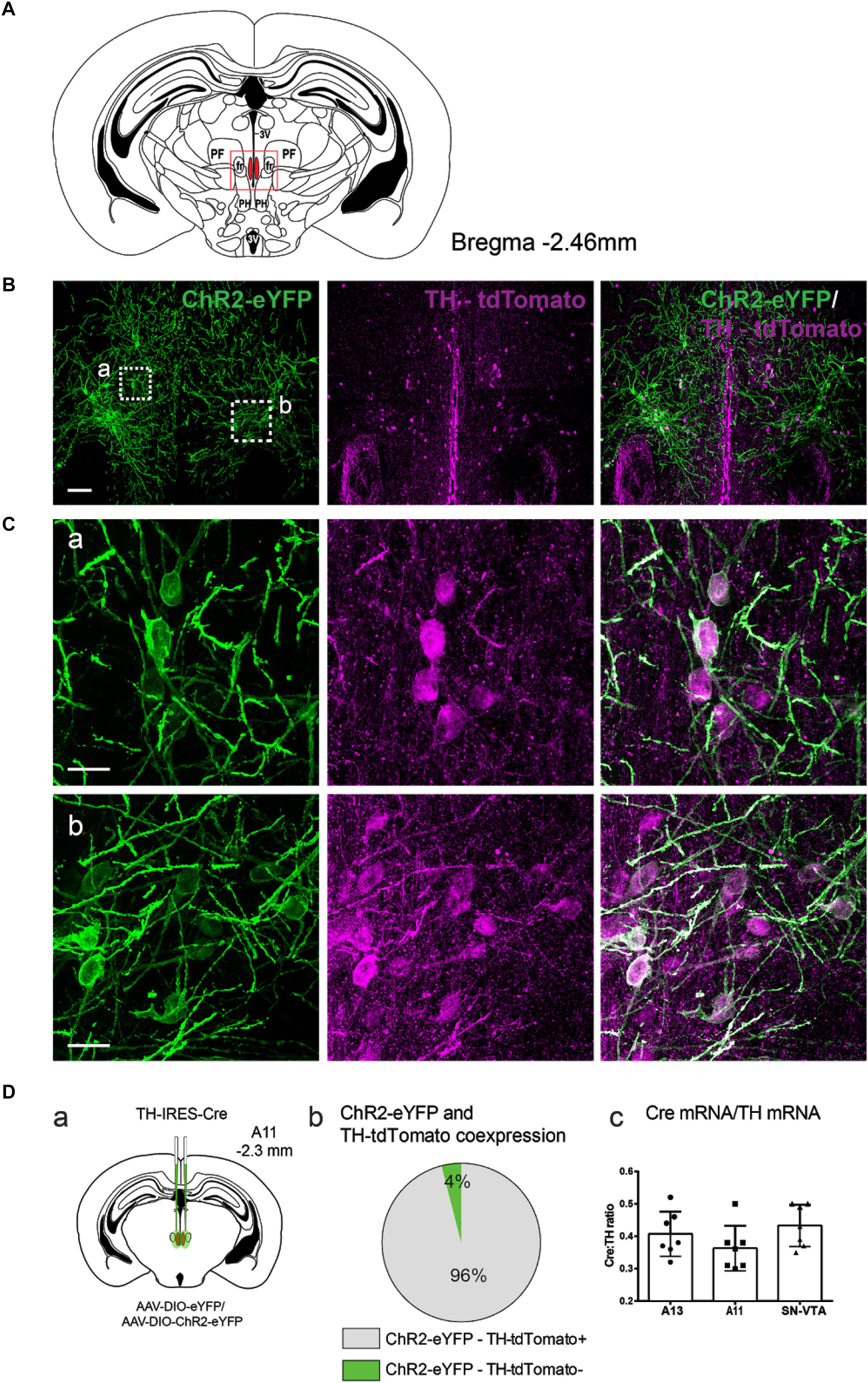
Frontiers | Optogenetic Activation of A11 Region Increases Motor Activity | Frontiers in Neural Circuits
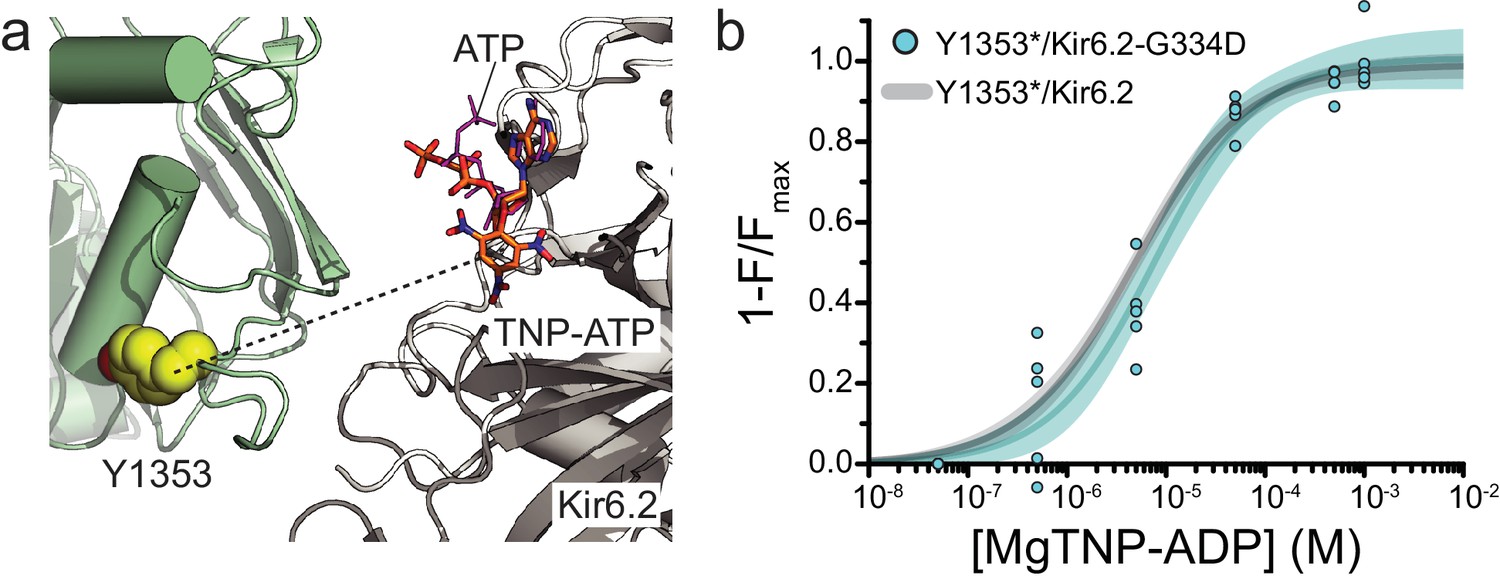
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife

The role of motile cilia in the development and physiology of the nervous system | Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
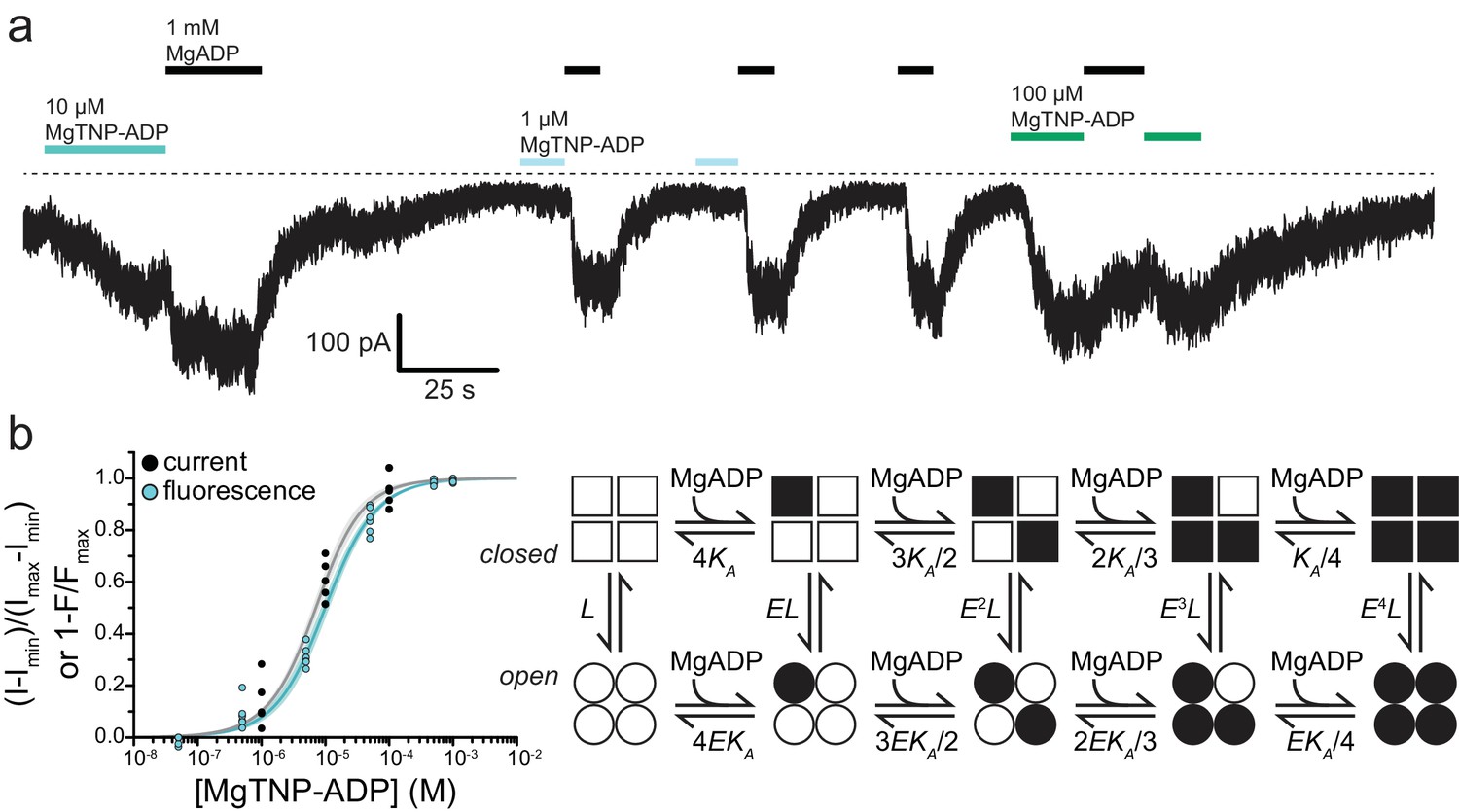
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife

Cancers | Free Full-Text | PARP1 Inhibition Augments UVB-Mediated Mitochondrial Changes—Implications for UV-Induced DNA Repair and Photocarcinogenesis | HTML
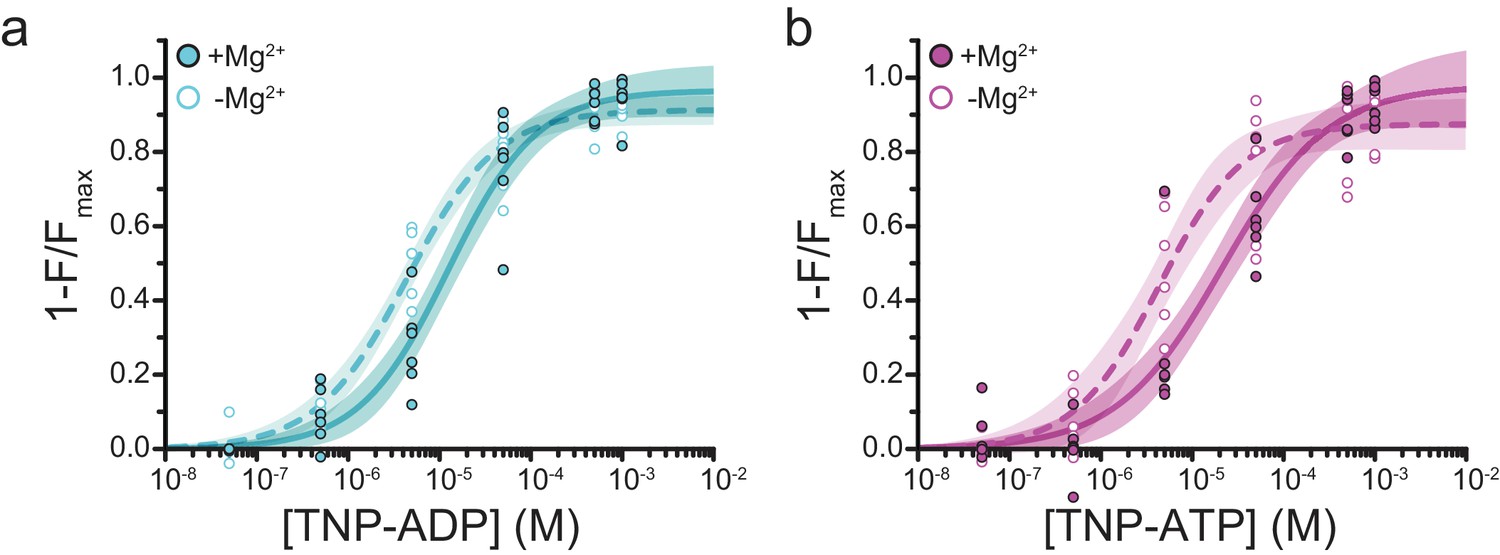
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife

Phospholipids as Modulators of KATP Channels: Distinct Mechanisms for Control of Sensitivity to Sulphonylureas, K+ Channel Openers, and ATP | Molecular Pharmacology
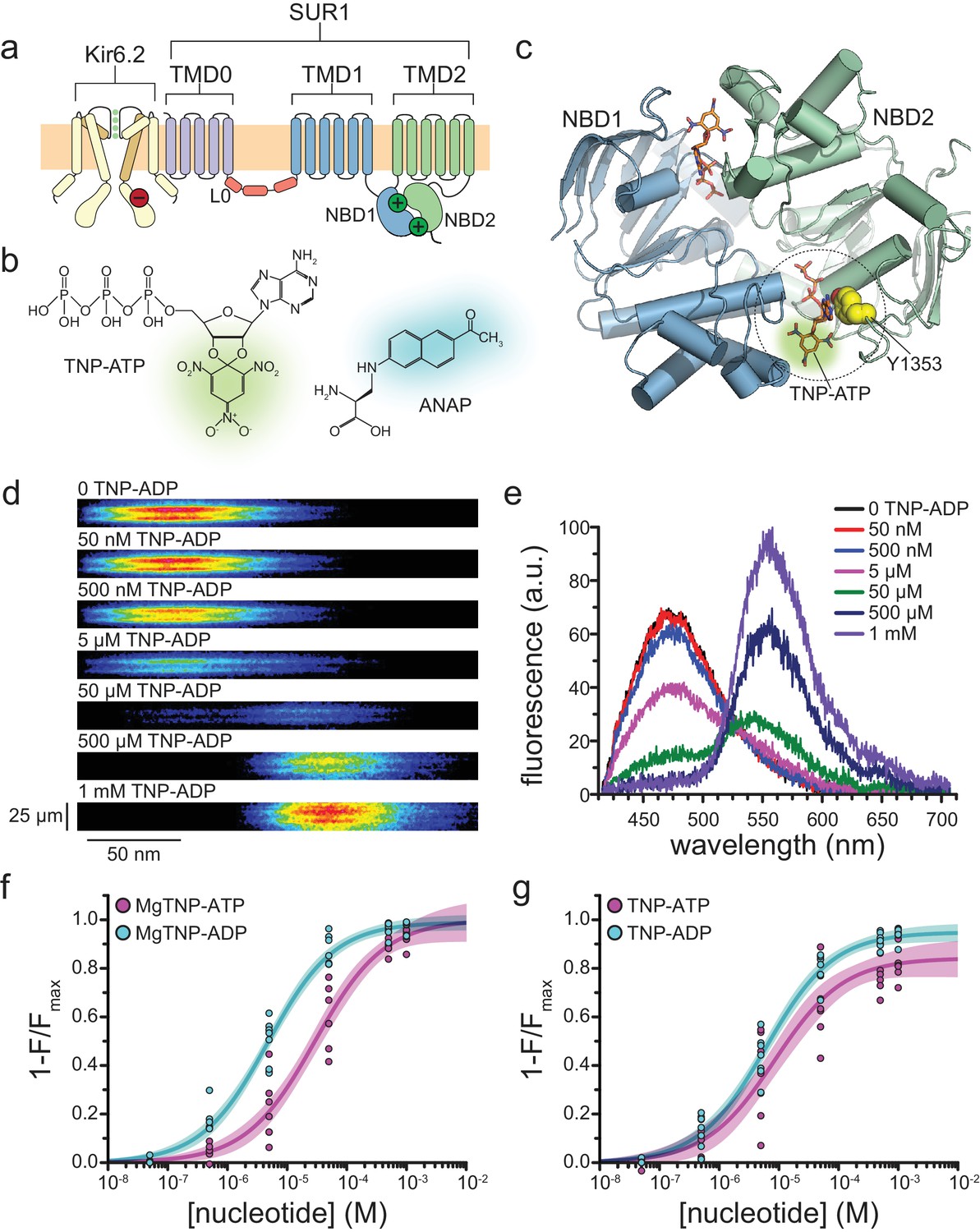
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife

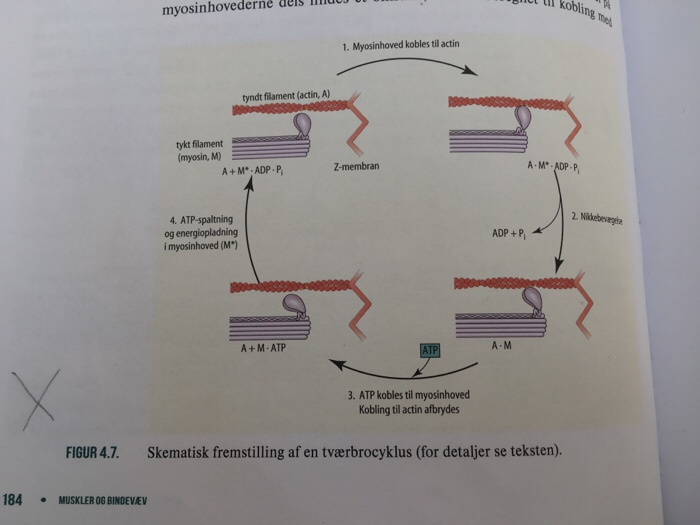
Bevis for en elektrostatisk mekanisme af kraftgenerering af bakteriofagen t4 dna emballagemotor - naturkommunikation | Kommunikation 2022

Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife

Hydrogen peroxide modulates synaptic transmission in ventral horn neurons of the rat spinal cord - Ohashi - 2016 - The Journal of Physiology - Wiley Online Library
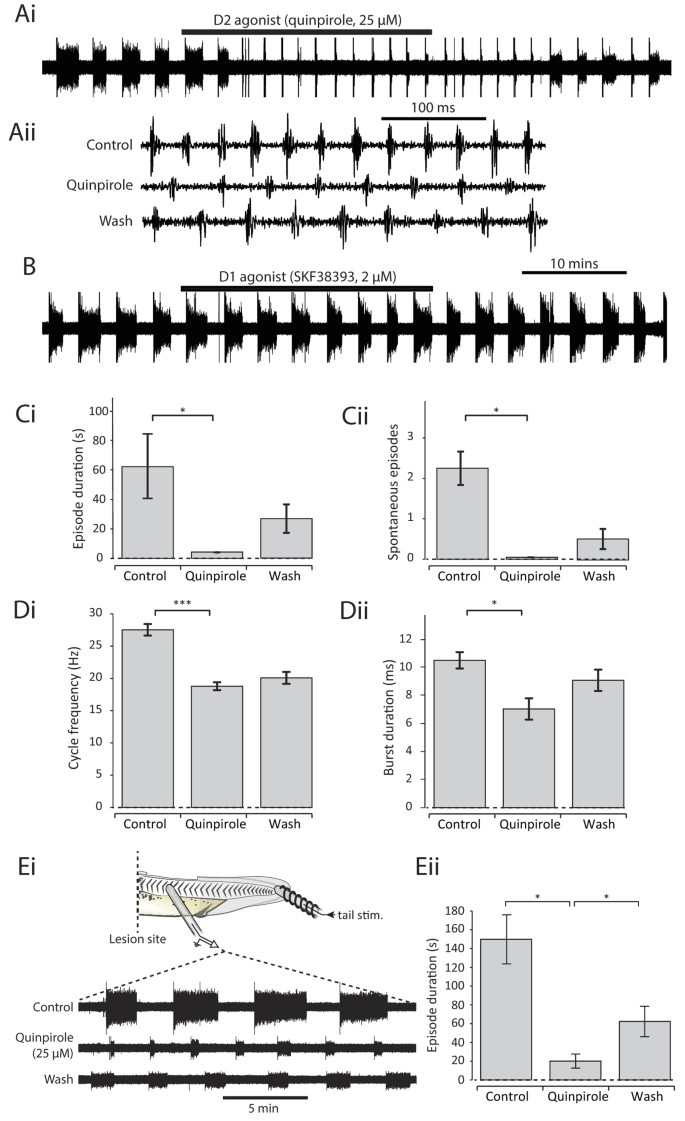
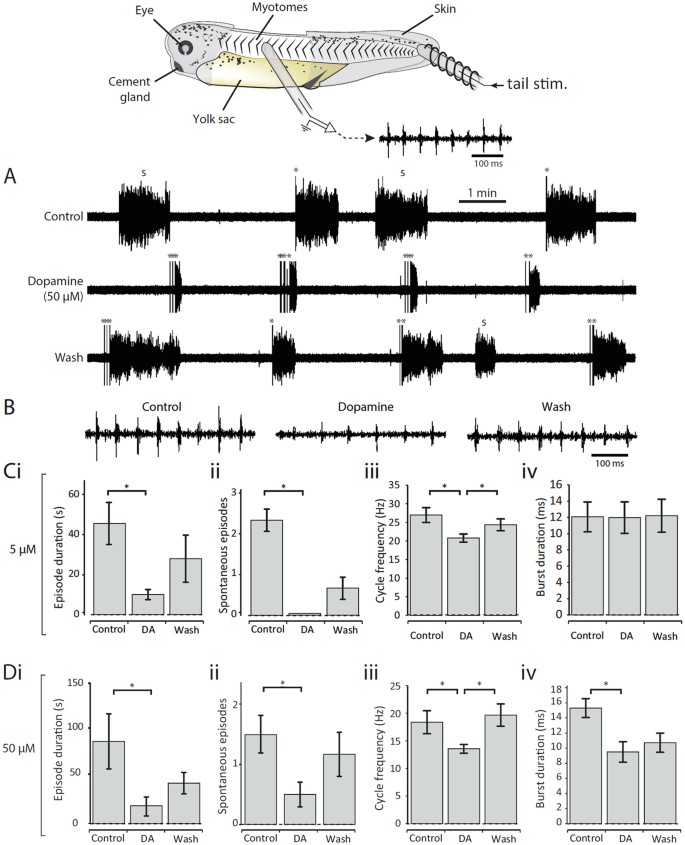
Mechanisms underlying the endogenous dopaminergic inhibition of spinal locomotor circuit function in Xenopus tadpoles | Scientific Reports

Dihydroergotamine affects spatial behavior and neurotransmission in the central nervous system of Wistar rats

The Novel Calcium Sensitizer Levosimendan Activates the ATP-Sensitive K+ Channel in Rat Ventricular Cells | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
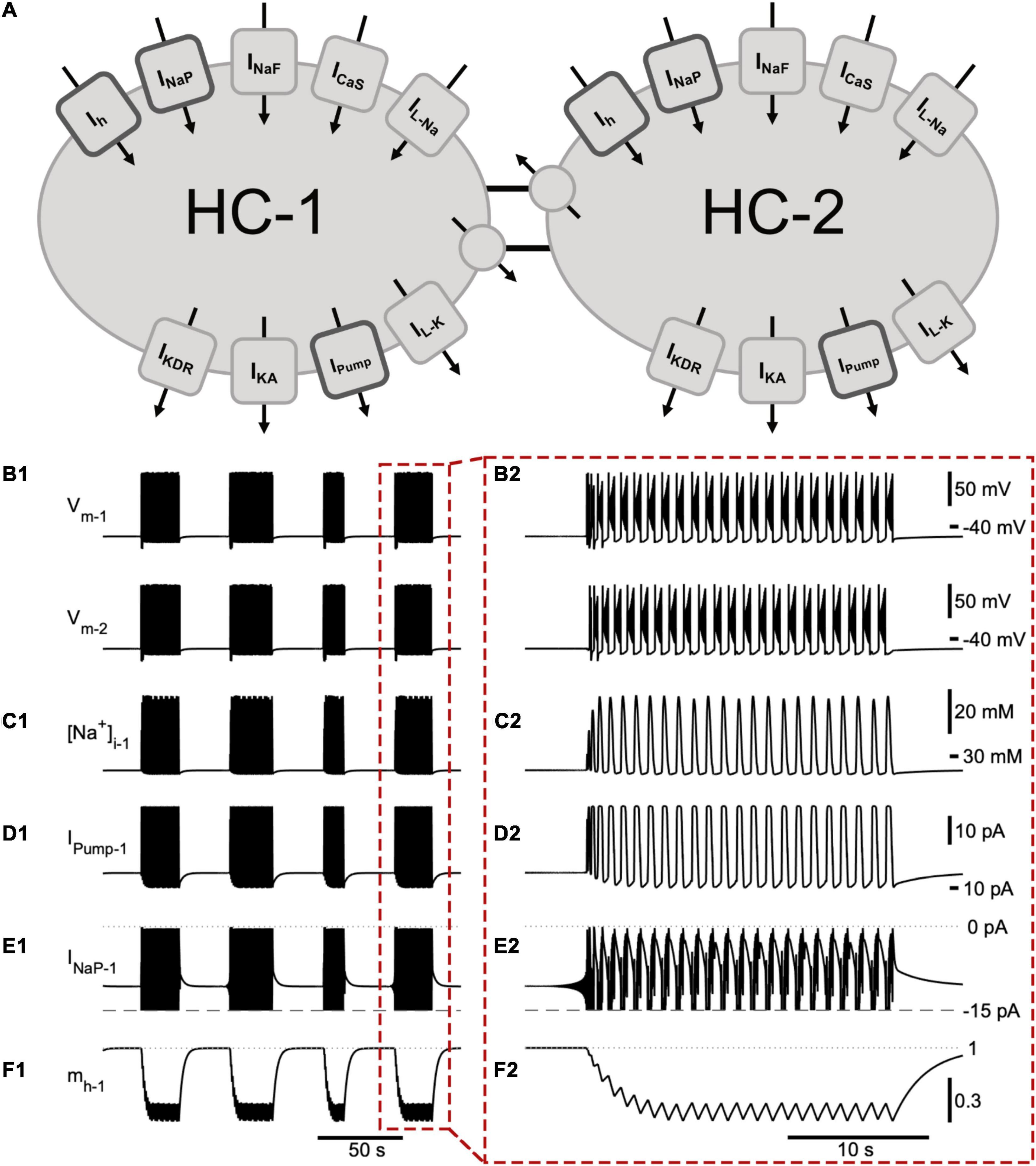
Frontiers | Contributions of h- and Na+/K+ Pump Currents to the Generation of Episodic and Continuous Rhythmic Activities | Cellular Neuroscience
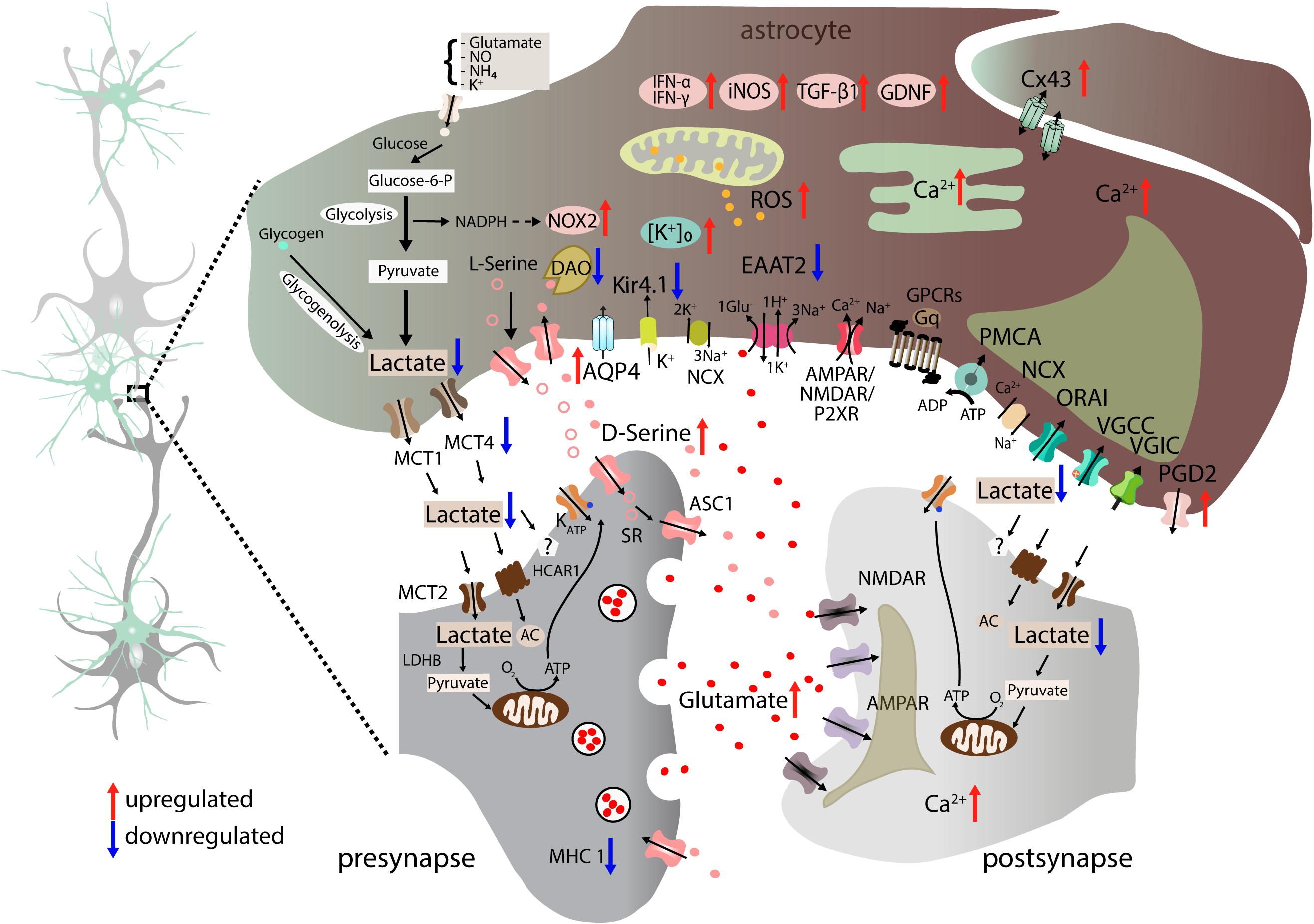
Frontiers | Exciting Complexity: The Role of Motor Circuit Elements in ALS Pathophysiology | Neuroscience
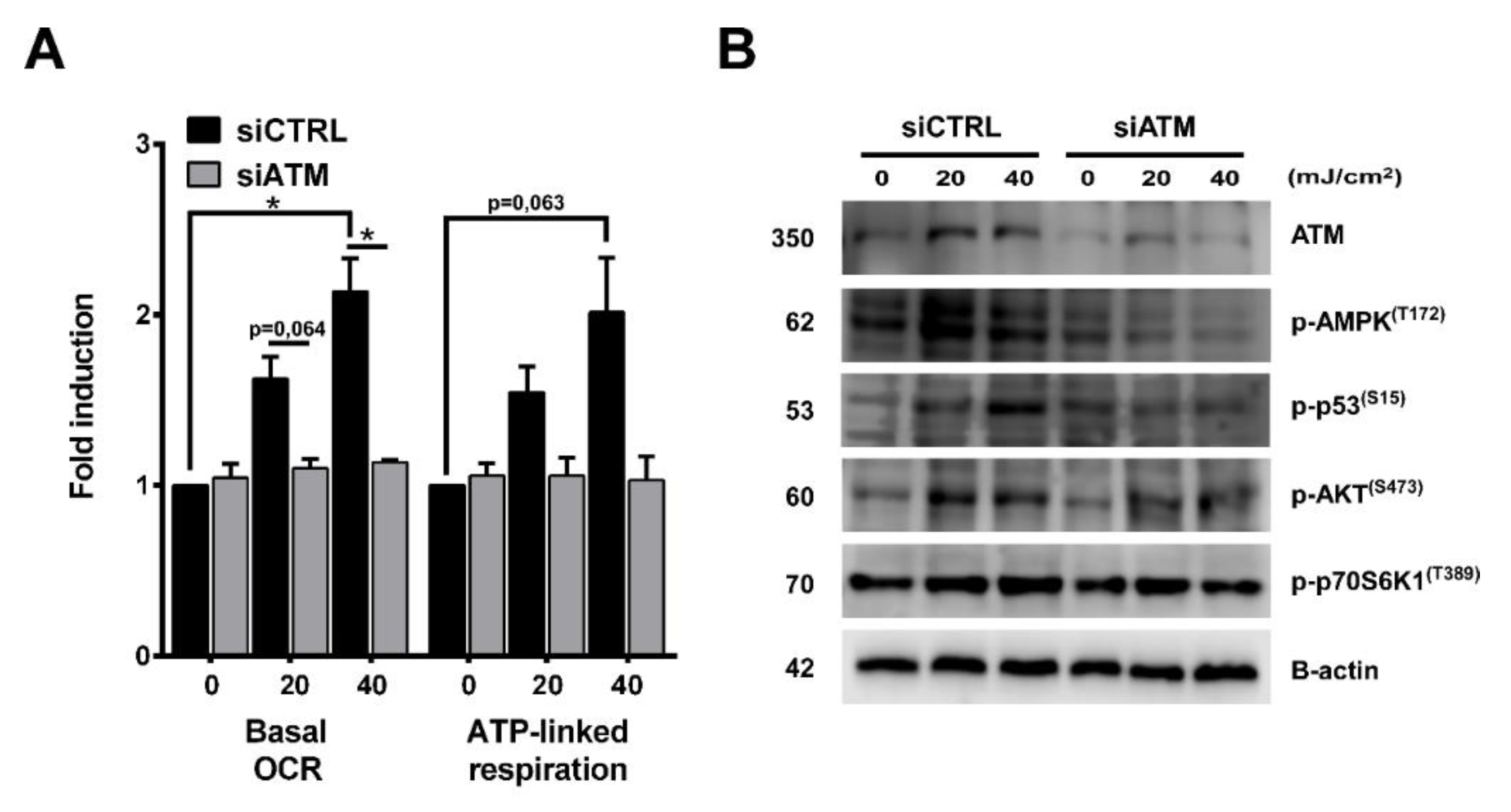
Cancers | Free Full-Text | PARP1 Inhibition Augments UVB-Mediated Mitochondrial Changes—Implications for UV-Induced DNA Repair and Photocarcinogenesis | HTML
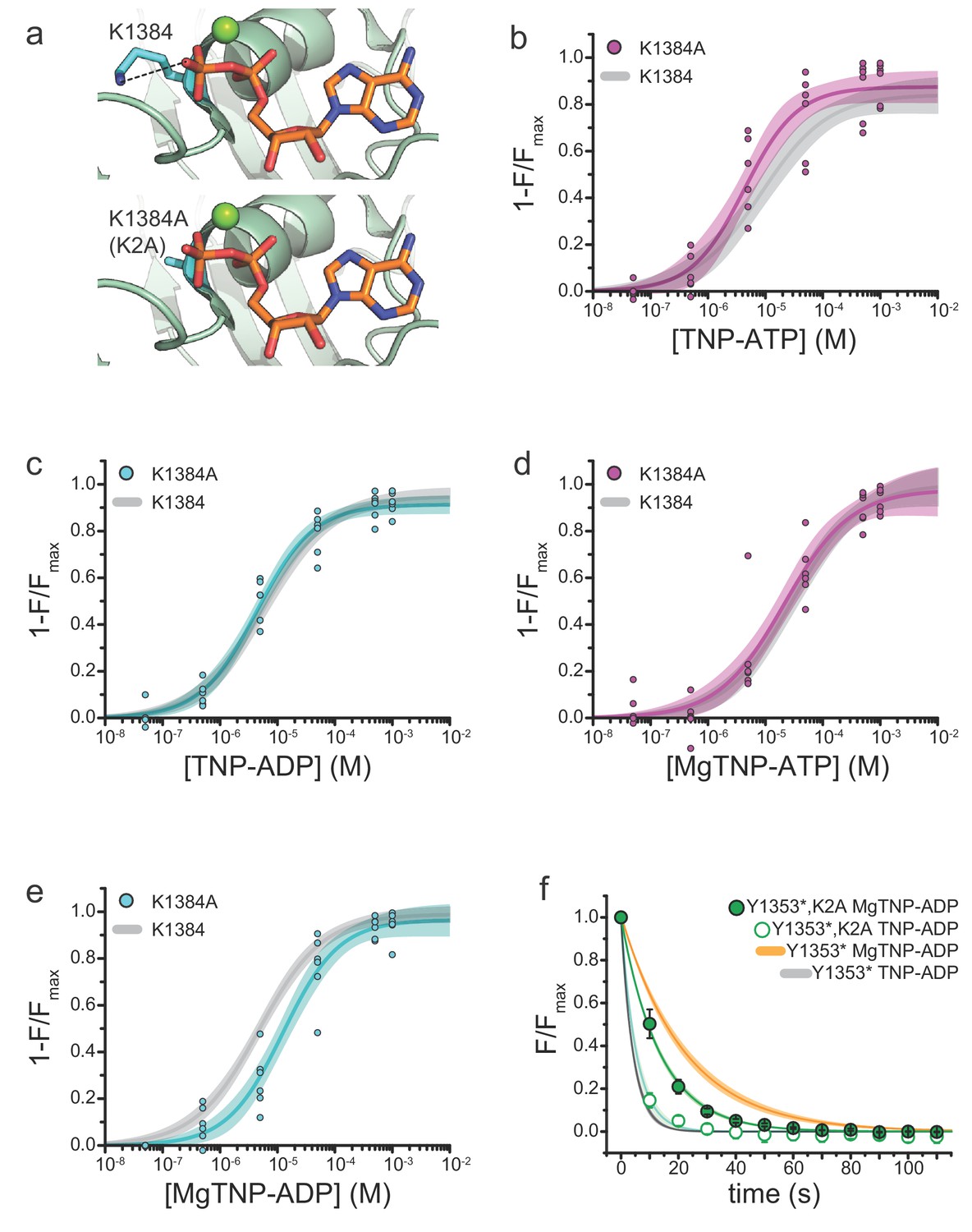
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife
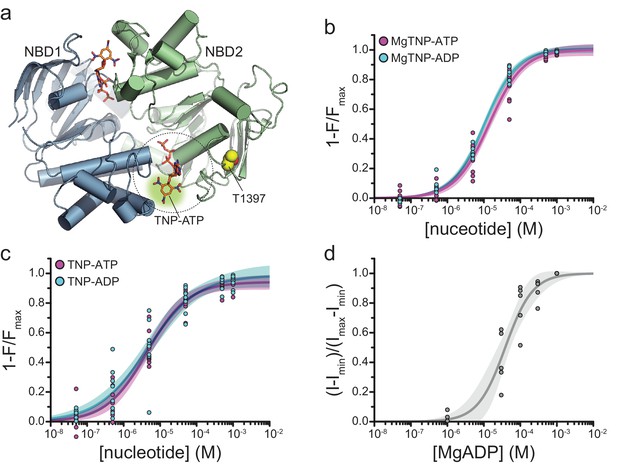
Activation mechanism of ATP-sensitive K+ channels explored with real-time nucleotide binding | eLife
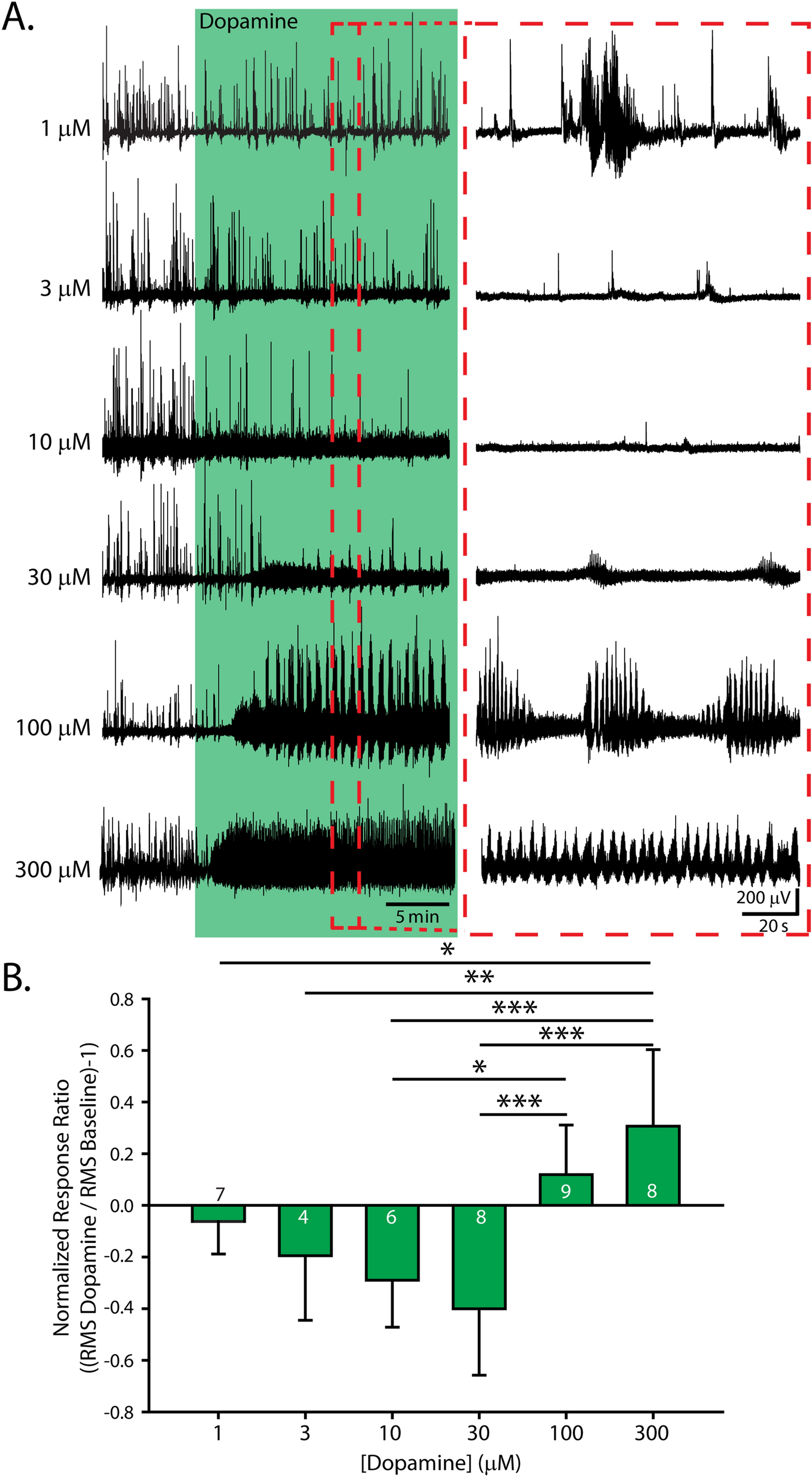
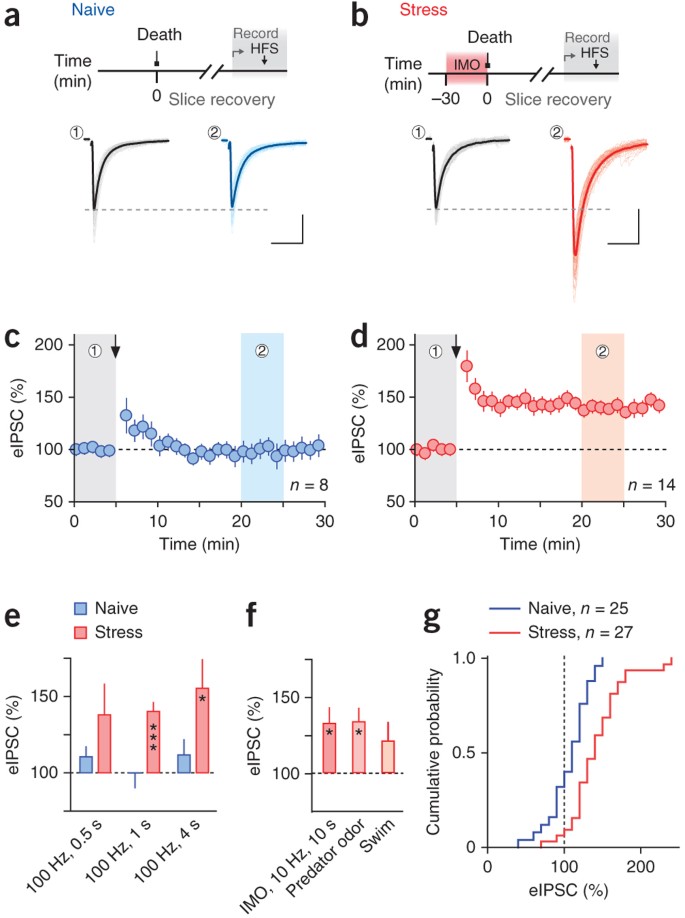
A dynamic role for dopamine receptors in the control of mammalian spinal networks | Scientific Reports